Some Common Sap Definitions
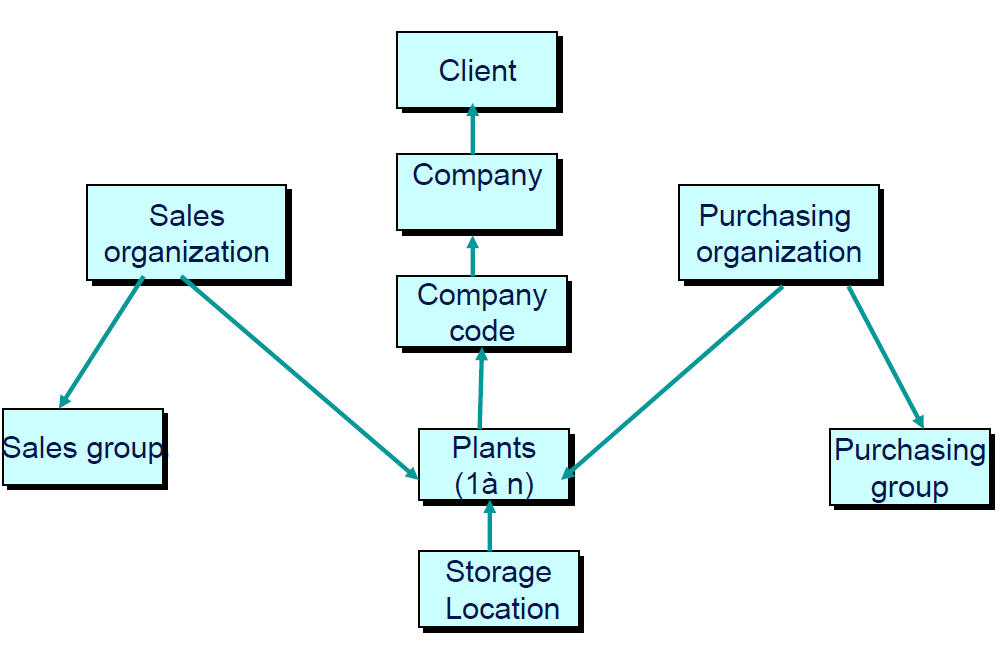
Client: is the highest level in the organization, it is enterprise which groups several companies.
Company Code: a company is a form of business organization, a company can be an association, partnership, or union that carries on a commercial or industrial enterprise.
General Ledger: is the main accounting record of a business which uses double-entry bookkeeping. It will usually include accounts for such items as current assets, fixed assets, liabilities, revenue and expense items, gains and losses.
Accounts Receivables: is one of a series of accounting transactions dealing with the billing of customers who owe money to a person, company or organization for goods and services.
Accounts Payables: is a file or account that contains money that a person or company owes to suppliers, but hasn’t paid yet.
Asset: it is property, plant, equipment or tangible assets these are purchased for continued and long-term use in earning profit in a business It also can be land, buildings, machinery, furniture, tools, and certain wasting resources e.g., timberland and minerals.
Asset Class: a company classifies it is assets to asset classes, every asset class contain number of assets which share the same attributes For example: class for land, vehicles, buildings and machines.
Group: it is group of accounts ’GL, AR or AP’ this accounts within the group have the same attributes, For ex: group for GL asset accounts Group for Local customers
Vendor: anyone who provides goods or services to a company. A vendor often manufactures inventory items, and sells those items to a customer.
Customer: A customer refers to individuals or households that purchase goods and services generated within the economy.
Cost Centre: Cost centers are divisions that add to the cost of the organization, but only indirectly add to the profit of the company. Typical examples include Research and Development and Marketing.
Profit Centre: are parts of a Corporation that directly add to its Profit.
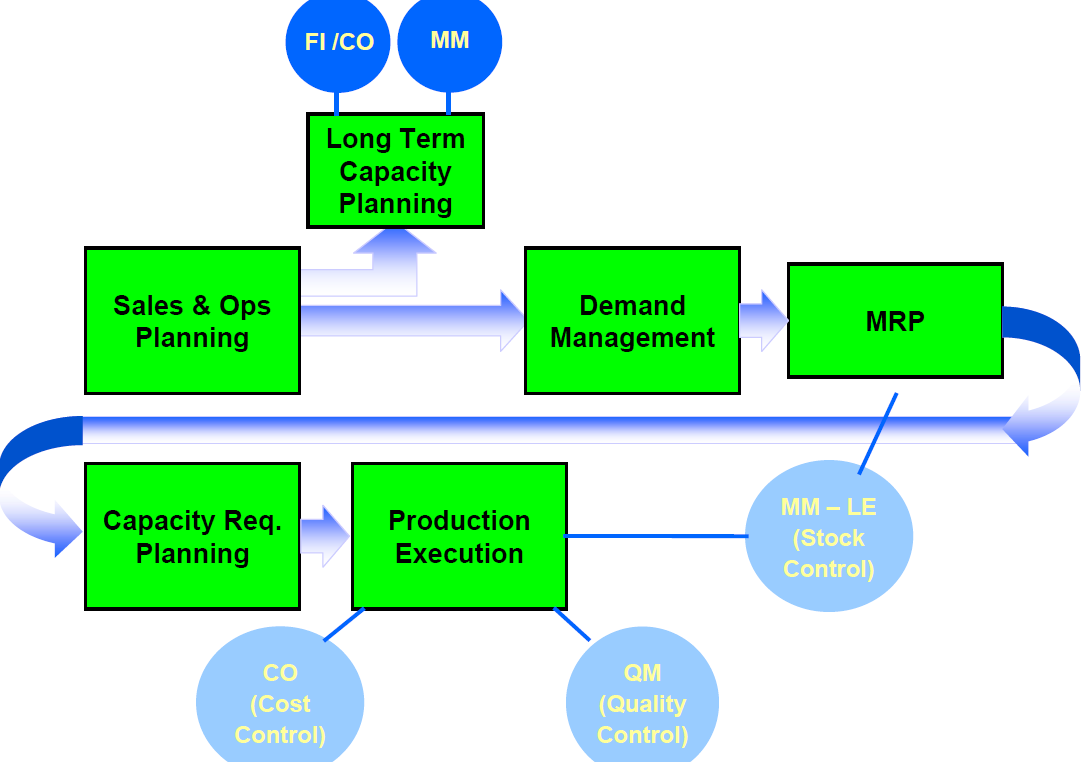
Posting: it is the last step in the document cycle in this step the document has effect on the financial accounting.
Parking: it is step between creating the document and posting it to Financial accounting in this step the document items has no effect on financial accounting also it will be valid for auditing and modification.
Posting Date: the day in which the document is completed’ Audited’ and posted to financial accounting.
Document date: it is the date in which the document created in.
Document Number: it is number specify specific document.
For example: the invoice number
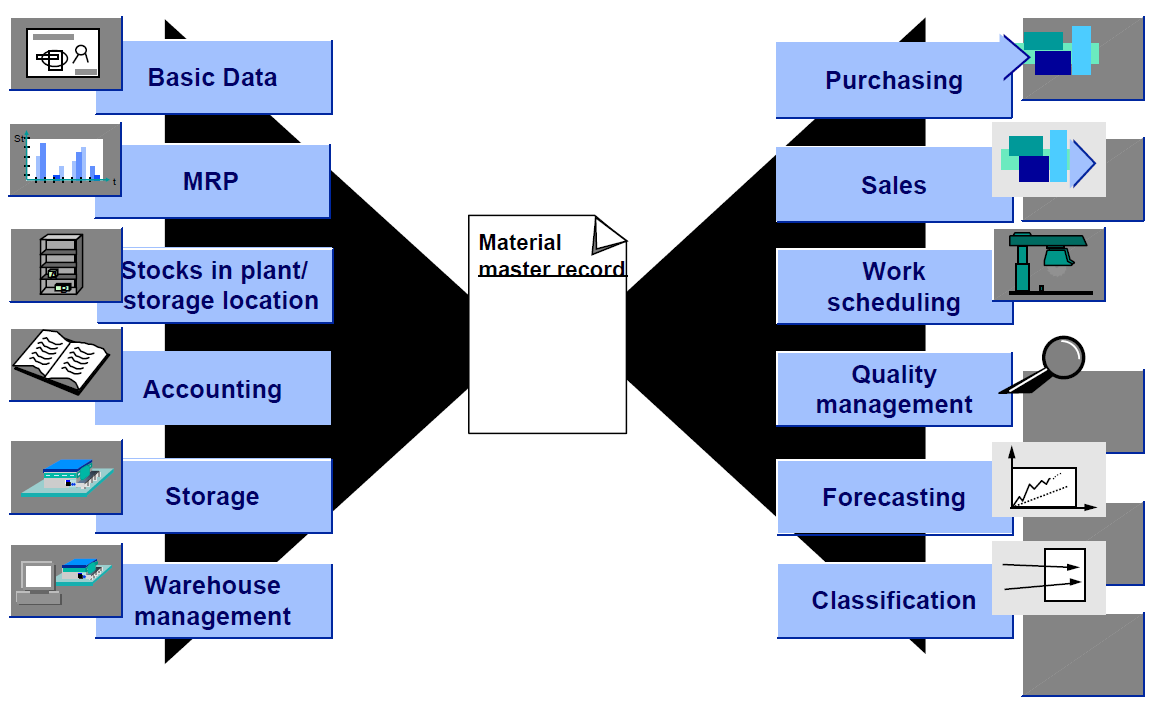
Line item: it is variable field within the screen display highlighting information. About the item, material, asset etc this information can display costing, grouping and dates.



Leave a Reply